CHRONICLE OF THE CATHOLIC CHURCH IN LITHUANIA NO. 32 
In This Issue:
Whats New in the Church's Life?
Socialism "Guarantees" Freedom of Conscience
Congratulations to The Chronicle of Current Events
Additional Information on the Trial of Vladas Lapienis, J. Matulionis and Ona Pranskūnaitė
From the Archieves of the Chronicle of the Catholic Church in Lithuania
SITUATION OF CATHOLICS IN MOLDAVIA
Lithuania ........................................... March, 1978

CHRONICLE OF THE CATHOLIC CHURCH IN LITHUANIA No. 32
A Translation of the Complete Lithuanian Original, LIETUVOS KATALIKŲ RAŽNYČIOS KRONIKA No. 32 Documenting the Struggle for Human Rights In Soviet-Occupied Lithuania Today
Translated by: Vita Matusaitis Translation Editor: Rev. Casimir Pugevičius Published by the Lithuanian R.C. Priests' League of America 351 Highland Rlvd. Rrooklyn, NY 11207
©Lithuanian Roman Catholic Priests' League of America 1978
Printed by Franciscan Fathers Press 341 Highland Blvd. Brooklyn, NY 11207
CHRONICLE OF THE CATHOLIC CHURCH IN LITHUANIA No. 32
Introduction
In 1940, when the Soviet Union occupied Lithuania by force, 85.5% of the country's more than 3 million inhabitants were Roman Catholic, 4.5% Protestant, 7.3% Jewish, 2.4% Orthodox and 0.2% of other persuasions.
In the two archdioceses and four dioceses were: 708 churches, 314 chapels, 73 monasteries, 85 convents, three archbishops, nine bishops, 1271 diocesan priests, 580 monks, of whom 168 were priests. Four seminaries had 470 students. There were 950 nuns.
Nuns cared for 35 kindergartens, 10 orphanages, 25 homes for the aged, two hospitals, a youth center, and an institute for the deaf-mute.
On June 15, 1940, the Red Army marched into Lithuania; the independent government was replaced by a puppet regime.
On July 14-15 rigged elections were staged. On July 21, with the Red Army surrounding the assembly house, the new People's Diet "unanimously" declared Lithuania a Soviet Socialist Republic.
On June 27, 1940, the Church was declared separate from the state, and the representative of the Holy See was expelled.
Parish lands were confiscated, clergy salaries and pensions were cut off, and their savings confiscated. Churches were deprived of support. Catholic printing plants were confiscated and religious books destroyed.
On June 28, 1940, the teaching of religion and recitation of prayers in schools was forbidden. The University's Department of Theology and Philosophy was abolished, and all private schools were nationalized. The seminaries at Vilkaviškis and Telšiai were closed, and the seminary at Kaunas was permitted to operate on a very limited scale. The clergy were spied upon constantly.
On June 15, 1941, 34,260 Lithuanians were packed off in cattle-cars to undisclosed points in the Soviet Union. After World War II, the mass deportations resumed and continued until 1953.
ecclesiastical forms of administration. In reality, all decisions are made by the state-appointed Deputy for Religious Affairs— an atheist.
It is the story of the struggle between clergy who have decided for one reason or another to cooperate with the regime, and stubborn dissident priests and faithful insisting on rights under the Soviet Constitution, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, and Natural Law.
It is the record of heroic parents of children, who insist on rearing their offspring in the Catholic Faith, against all efforts by teachers and government youth leaders to dragoon youngsters into various Communist youth organizations.
The Chronicle is the record of mere school children risking the wrath of atheistic teachers and even of Security police, to go to church or sing in a choir.
Constantly harassed in one way or another, the religious believers of Lithuania find themselves in the position of second-class citizens.
Denied access to mass media to tell their story, or to religious literature to nourish their faith, the Catholics of Lithuania find it necessary to photo-copy such religious literature as they can lay their hands on.
Ironically, the Soviet constitution, under which the people of Lithuania are forced to live, contains glowing guarantees of freedom of conscience, of assembly, of press, and of speech.
In practice, such constitutional guarantees are over-ridden by unwritten administrative decrees, verbal interpretations, and galling bureaucratic high-handedness, giving atheism the position of the established religion of the Soviet Union and its subject territories.
The message of the Chronicle, loud and clear, is that the atheistic government is slowly strangling the Church in Lithuania, while doing its best to make it look like the Church is dying a natural death. The people of Lithuania are risking imprisonment, labor camp, and torture to make sure that we are not deceived.
Rev. Casimir Pugevičius Translation Editor
INDEX OF PERSONS
Budriūnas, Rev. Petras 18-20
Buzaitė, Janina 24-25
Černiauskas, Rev. V. 38
Gražulis, Antanas 9
Janulis, Rev. Juozas 18-24
Jurevičius, Mečislovas 26-27
Krikščiūnas, Kastytis 9
Lapienis, Vladas 10, 12-16
Laurinavičius, Rev. B. 27-32
Mačiulis, Antanas 16, 17-18
Matulionis, A. 15
Oleinik, Valentina 49-52
Plumpa, Petras 28
Pranckūnaitė, Ona 12, 14-16
Pūkas, Vytautas 5, 10
Ražukas, Petras 5, 9-10
Ribickaitė, Birutė 39
Sadūnaitė, Nijolė 29
Senovaitienė, Julija 19
Sraurylaitė, Marytė 19
Steponavičius, Bishop Julijonas 29
Strazdas, Povilas 19
Vitkūnaitė, Marytė 7-9
Ylius, Rev. A. 25-26
Žalaitė, Rita 22-23
Zavalniuk, Rev. Vladislus 46-52
INDEX OF PLACES
Adutiškis, 27-33
Anykščiai 18-24
Deltuva, 27
Kapsukas 24-25
Klausučiai 33-34
Kvėdarna 36-37, 39-40
Mažeikiai 37
Paringys 16-18
Raudėnai 36
Sartininkai 41
Šiauliai 25-26
Širvintos 37-38, 42
Telšiai 25, 35-36, 38-39
Viešvėnai 40-41
Vilkaviškis 41-42
Žalioji 34-35
Žemaičių Kalvarija 42
TO HELP THE CHURCH IN COMMUNIST-OCCUPIED LITHUANIA OR TO OBTAIN FURTHER INFORMATION, SEND YOUR TAX-EXEMPT DONATION, OR WRITE TO:
Lithuanian Catholic Religious Aid, Inc. 351 Highland Boulevard Brooklyn, NY 11207
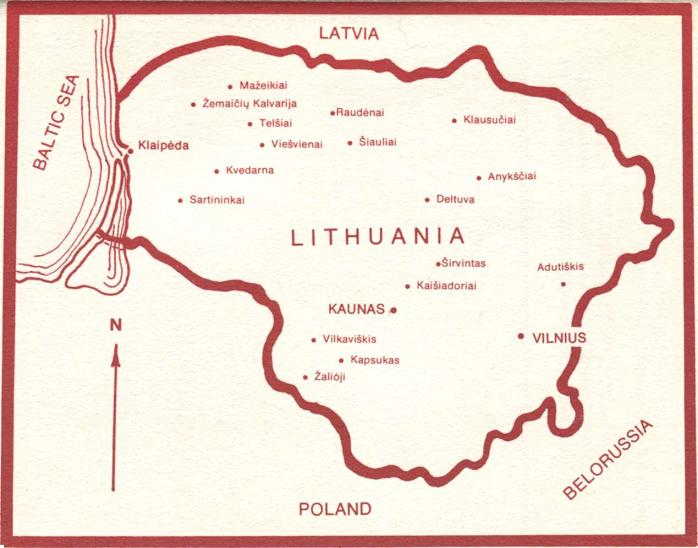
Places mentioned in the Chronicle of the Catholic Church in Lithuania No. 32